Firefighting could seem pretty diverse in the long term, because of to clever fireplace suits and masks established by several exploration institutions in China.
Scientists from multiple institutions address the worries and restrictions of latest fire-preventing gear by introducing wearable, breathable sensors and electrodes to better serve firefighters. Picture Credit history: Nano Investigate, Tsinghua University Push.
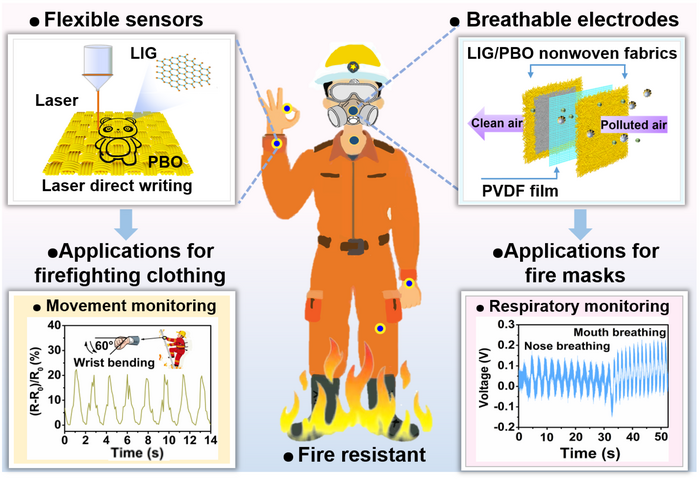
Researchers published findings demonstrating that breathable electrodes woven into fabric applied in fire suits are steady at temperatures over and above 520 ºC. The fabric is typically non-flamable at these temperatures, with significant charges of thermal safety at the greatest time documented so significantly for these technological know-how: 18.91 seconds.
The study was released in the journal Nano Exploration on January 12th, 2023.
The findings demonstrate the performance and practicality of Janus graphene/poly(p-phenylene benzobisoxazole), or PBO, woven material in earning firefighting “smarter,” with the major objective staying to make products and solutions on an industrial scale that are not only flame-retardant but also intelligent plenty of to inform the firefighter of increased risks though traversing the flames.
Regular firefighting clothes and fireplace masks can make certain firemen’s security to a specified extent. However, the fireplace scene generally changes quickly, from time to time producing firefighters trapped in the hearth for failing to judge the hazards in time. At this predicament, firefighters also require to be rescued.
Wei Lover, Professor and Researcher, Faculty of Textile Science and Engineering, Xi’an Polytechnic University
The utilization of Janus graphene/PBO woven fabrics is critical. Even though not the 1st of its form, the use of PBO fibers supplies extra strength and fireplace resistance than other associated fibers like Kevlar. PBO fibers are woven into a cloth before currently being irradiated with a CO2 infrared laser. The cloth is then transformed into the Janus graphene/PBO hybrid which is the focus of the investigation.
The mask also has a Janus graphene/PBO top rated and bottom layer with a piezoelectric layer in between that converts mechanical pressures to electrical energy and vice versa.
The mask has a good smoke particle filtration impact, and the filtration performance of PM2.5 and PM3. reaches 95{5e37bb13eee9fcae577c356a6edbd948fa817adb745f8ff03ff00bd2962a045d} and 100{5e37bb13eee9fcae577c356a6edbd948fa817adb745f8ff03ff00bd2962a045d}, respectively. In the meantime, the mask has excellent carrying consolation as its respiratory resistance (46.8 Pa) is lower than 49 Pa of professional masks. Moreover, the mask is sensitive to the pace and intensity of human breathing, which can dynamically monitor the wellness of the firemen.
Wei Admirer, Professor and Researcher, School of Textile Science and Engineering, Xi’an Polytechnic College
Flame-retardant electronics utilized in these fire suits are versatile, heat resistant, straightforward to manufacture, and minimal-price tag, building scaling for industrial generation a possible accomplishment. This raises the chance that long term firefighting fits and masks will be in a position to utilize this engineering successfully. Fast, powerful interventions can also support to avert financial losses caused by fires.
The graphene/PBO woven materials-based sensors exhibit very good repeatability and stability in human motion monitoring and NO2 gasoline detection, the primary toxic gas in fires, which can be used to firefighting satisfies to assistance firefighters proficiently avoiding hazard.
Wei Admirer, Professor and Researcher, University of Textile Science and Engineering, Xi’an Polytechnic University
The potential to detect sudden surges in NO2 gas can allow firefighters to change study course in an instantaneous if important, and it could be a lifesaving addition to firefighter equipment.
Working with graphene/PBO woven and nonwoven fabrics, substantial improvements in firefighting can be accomplished to improved shield firefighters. The popular software of this technological innovation could assist researchers in their best target of reducing dying and injuries among the people who hazard their life combating flames.
Yu Luo and Wei Admirer contributed equally to the study along with Yaping Miao, Weichun Chen, and Yao Zhang of the School of Textile Science and Engineering at Xi’an Polytechnic University, Huiming Wang of the Division of Chemistry at Tsinghua University, Kai Dong of the Beijing Institute of Nanoenergy and Nanosystems at the Chinese Academy of Sciences, and Lin Hou and Yanyan Xu of Shaanxi Textile Analysis Institute Co., LTD.
This analysis was funded by the Countrywide Natural Science Foundation of China, Textile Vision Simple Research Program of China, Crucial Analysis and Development Plan of Xianyang Science and Know-how Bureau, Crucial Investigate and Advancement Plan of Shaanxi Province, Normal Science Basis of Shaanxi Province, and Scientific Exploration Project of Shaanxi Provincial Education Office.
Journal Reference
Luo, Y., et al. (2023) Laser-induced Janus graphene/poly(p-phenylene benzobisoxazole) fabrics with intrinsic flame retardancy as versatile sensors and breathable electrodes for hearth-combating discipline. Nano Research. doi.org/10.1007/s12274-023-5382-y.

